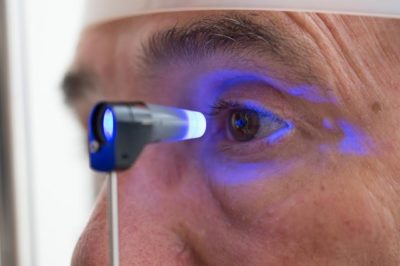
Glaucoma is an eye disease that causes loss of sight by damaging a part of the eye called the optic nerve. Glaucoma often presents as a silent killer and once lost vision cannot be restored.
Risk factors:
- Age: More frequently seen in older age groups
- Race: African-Americans have higher occurrence of Glaucoma
- Family history: First degree relatives having Glaucoma warrants a thorough examination to rule out Glaucoma in other family members
- Medical history: Previous eye injuries, eye surgery or long-term steroid use anywhere in the body can increase risk of glaucoma
Investigations:
- Tonometry: Procedure in which pressure of the eye is measured
- Pachymetry: Measurement of thickness of the cornea (the front window of the eye)
- Ophthalmoscopy: Examination of the Optic nerve head after dilation of pupil
- Gonioscopy: Examination of drainage angle of the eye
- Perimetry: Evaluates your visual field
Treatments:
Glaucoma can usually be treated and controlled using medicine(s), laser surgery, Glaucoma surgery or a combination of these treatments. Medicines (eye drops) are typically the first step in treatment, but laser surgery may be just as effective as a first choice. Your treatment should be as per the advice of your doctor
There are three common laser procedures:
- Laser trabeculoplasty
- Peripheral iridotomy
- Laser cyclophotocoagulation
Glaucoma Surgeries:
- Filtering surgery
- Drainage implant surgery